- 27/03/2021
- Dr. Samrat Jankar
- 0 Comments
- Blog
All you need to know about Gallbladder Stones
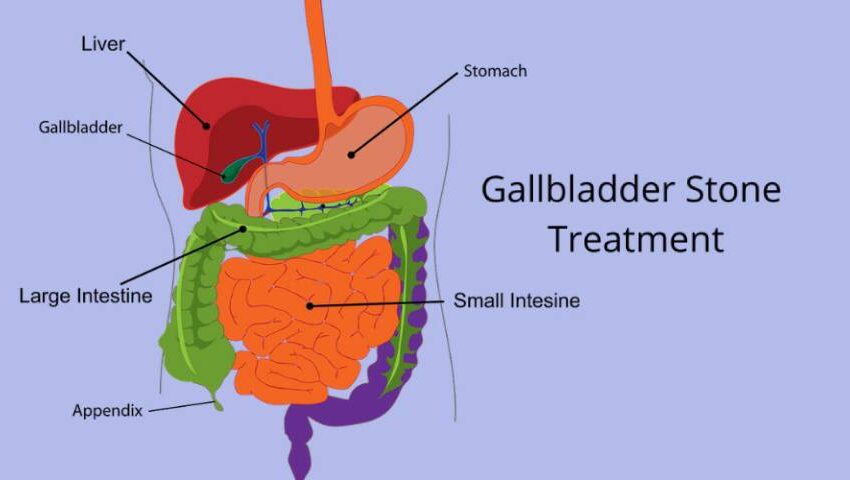
Gallstones are dense deposits that form in the gallbladder when the digestive fluid bile has a chemical imbalance. The gallbladder is a pouch-like organ situated under the liver. Bile formed by the liver is stored in the gallbladder.
The gallbladder is hollow and flat after meals, like a deflated balloon. The gallbladder can be full of bile and the size of a small pear before a meal.
Adults have seen an increase in their prevalence in recent years. Gallbladder stones can be effectively treated by a proficient Gastroenterologist in Pune. Gallstones are a risk factor for gallbladder cancer, accounting for nearly 10% of all cancer cases worldwide.
Gallstones have been discovered in 80% of GBC patients in India. Their involvement worsens cancer patients’ conditions and reduces their chances of survival.
This blog provides an overview of some of the causes, symptoms, prescribed treatment, and surgical options for gallbladder stones.
What Are Gallbladder Stones?
There Are Two Types Of Gallstones:
1. Cholesterol Stones
These develop when the gallbladder contains more cholesterol than the bile salts.
2. Pigment Stones
Patients with pre-existing liver disorders such as cirrhosis, biliary tract infections, and some forms of anaemia are more prone to develop pigment stones. These are composed of calcium salts and bilirubin.
What Causes Gallbladder Stones?
What are the Symptoms of Gallbladder Disease?
- Most gallbladder stone patients have “silent stones.” Therefore, remain asymptomatic for quite an extended period.
- When gallstone’s symptoms manifest, however, they can be unbearable and painful.
- They may also cause complications and long-term effects, including infection, gallbladder inflammation, and gallbladder cancer.
The Following Are Some Symptoms Of Cholelithiasis:
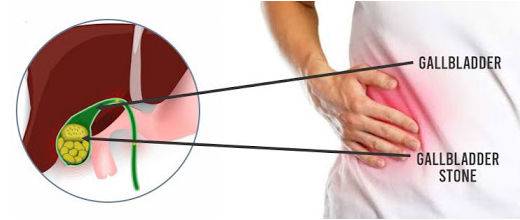
- Biliary colic- It is a form of abdominal pain that occurs in the abdomen’s upper right side
- Fatty food intolerance
- Pressure in the area between the shoulder blades
- Nausea and vomiting
- Build-up of gas in the intestines (flatulence)
- Fever and chills
- Sweating
- Yellowing of the eyes and skin (jaundice)
- Tea-colored urine
- Clay-colored stools
Who Is at Risk of Developing Gallbladder Stones?
Following people are more prone to acquire gallbladder stones:
- Men over the age of 60
- Women aged 20 and over
- Overweight
- Pregnant women
- Women who have undergone estrogen replacement therapy
- Women who have used birth control pills
- People who have lost weight quickly by going on strict diets
How Are Gallbladder Stones Diagnosed?
To diagnose gallstones, a gastroenterologist can use a combination of lab and imaging tests. The following are some of the tests that can be used to diagnose the gallstones:
- Blood tests to check blood count or measuring levels of amylase or lipase enzymes (vital digestive enzymes)
- Ultrasound to capture images of the gallbladder
- CT-scan for creating detailed images of abdominal organs
- HIDA scan or cholescintigraphy to test bladder emptying function
- MRCP to generate clear images of the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder
- ERCP is an invasive test to help locate and treat bile and pancreatic duct problems.
Treatment for Gallbladder Stones
Some gallstones treatment options may include:
- Oral bile acids like ursodiol and chenodiol are used in conventional medicine.
- Non-surgical options include MTBE injections, ERCP, percutaneous cholecystostomy.
- In rare cases, shock wave lithotripsy shatters massive gallstones into small fragments.
- The gallbladder is removed during surgery (Cholecystectomy).
Surgical Procedures
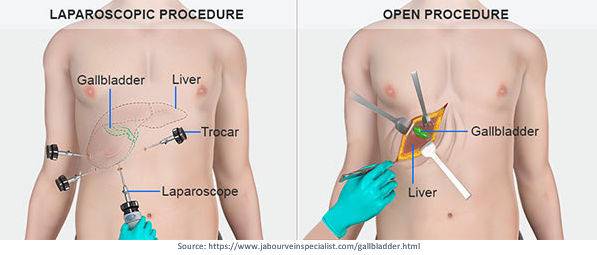
If gallstones recur, surgery to remove the gallbladder, or Cholecystectomy, may be recommended. There are Two Forms of Cholecystectomy:
1. Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
It is a minimally invasive procedure performed by a laparoscopic surgeon in Pune.
2. Open Cholecystectomy
It is advised when the gallbladder is seriously swollen, inflamed, or scarred from previous procedures.
How Can Gallbladder Stones Be Prevented?
Many gallstone disease risk factors, such as age, gender, and genetics, cannot be changed to prevent gallstone formation. On the other hand, gallstones can be efficiently managed and prevented by:
- Following a nutritious diet that emphasizes high-fibre foods and healthy fats.
- Fried foods, processed meats, high-fat dairy products, refined carbs, alcohol, and sugar are all foods that should be avoided.
- Maintaining a healthy weight by exercising daily.
- Smoking may lead to the formation of gallbladder stones, so avoid it.
