
- 23/02/2021
- Dr. Samrat Jankar
- 0 Comments
- Blog
Stomach cancer – All you need to know
Here, in this article, we are going to discuss stomach cancer. Read the article to know in detail.
Stomach cancer is abnormal cell growth that multiplies in number very rapidly. It forms a mass in the stomach. The survival rate for stomach cancer is less than 10% worldwide.
Stomach cancer usually develops in the mucus-forming cells situated in the line of the stomach. This type is responsible for 90 to 95 percent of all stomach cancers. It is also known as gastric cancer.
Stomach cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer and the third leading cause of cancer-related death across the globe. It is difficult to diagnose, as it does not produce any early symptoms. By the time symptoms generate, cancer would have reached an advanced stage and may have spread to other organs.
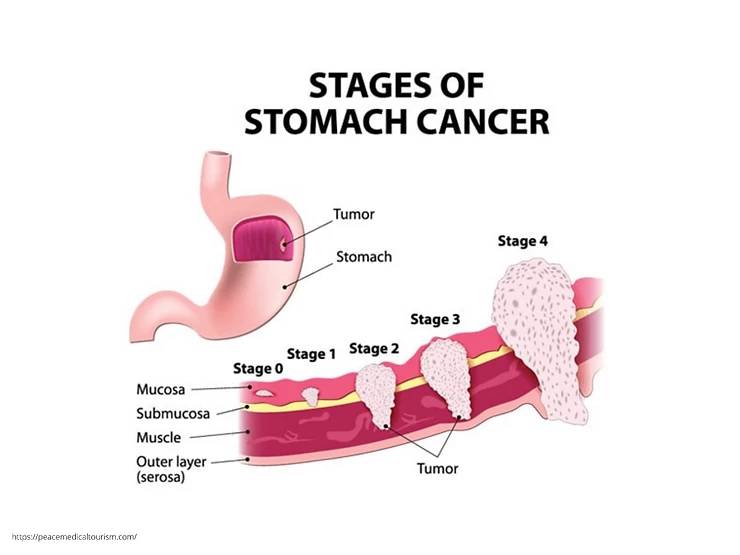
Stomach cancer is prevalent in East Asia and Eastern Europe. It occurs twice as often in males than in females. There are four stages of stomach cancer Stage 1 2 3 & 4 cancer.
Stomach cancer develops when cancer cells grow in the stomach’s inner lining. These cells have the potential to develop into a tumor. The disease, also known as stomach cancer, normally progresses slowly over several years. People in their late 60s and early 80s are most likely to get stomach cancer.
Stage 1 is limited to the top layer of tissue located at the inside of the stomach.
Stage 2 cancer spreads more profound into the muscle layer of the stomach wall.
Stage 3 cancer may grow through all the stomach layers and applies to structures surrounding the stomach.
Stage 4 indicates that cancer has spread into other body parts.
Stomach cancer starts when a problem develops in the structure of your DNA. When this happens, the affected gene becomes unable to control cellular dynamics. As a result, it produces new cells uncontrollably. It is not entirely clear why stomach cells become cancerous in some people.
What are the causes of stomach cancer?
Certain factors are qualified to be the risk factors for stomach cancer including
- Oesophagus inflammation of the inner lining of the stomach
- Severe anemia
- A history of stomach ulcers
- Family history of stomach cancer
- Long-term smokers
- Excessive consumption of salty foods
- Consumption of smoked meats and pickled vegetables
- Bacterial infection into your stomach inner wall
- Stomach polyps
- Development of lymphoma tumors
What are the symptoms?
Stomach cancer can occur with a feeling of being full during meals, even with a small food intake. Gradually the patient may experience
- Difficulty with swallowing
- Frequent burping
- Indigestion
- Stomach-ache
- Heartburn
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloody stool
- Constant bloating
- Feeling full after eating a small amount of food
On reaching a more advanced stage, stomach cancer can cause
- Fatigue
- Anemia
- Black stools
- Loss of appetite
- Significant weight loss
There may be blood mixed or dark-colored vomiting. That most likely signifies bleeding from the Stomach. Individuals with these signs and symptoms are prone to stomach cancer. They must consult their doctor at the earliest.
How to diagnose stomach cancer?
To make the diagnosis our doctor looks at your medical history, examines you thoroughly, and conducts a few tests such as
- Routine lab tests
- Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Imaging tests which may include CT scan and a particular type of x-ray called a barium swallow
- A scabby test to visualize your stomach and look for signs of cancer
If we find any suspicious areas, then a biopsy is compulsory to check if your cancer has metastasized You may require Exploratory surgery also
What are the treatments available for stomach cancer?
Stomach cancer treatment includes the following procedures-
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Immunotherapy uses medicines that recruit a person’s immune system to find and destroy cancer cells. Targeted therapies use drugs that block the growth and spread of cancer by selectively destroying the cancer cells directly or preventing them from multiplying.
The exact treatment plan depends on the stage of cancer and other factors such as the patient’s age and overall health condition. Chances of recovery are always better if we can diagnose cancer in the early stages. Once cancer reaches the advanced stage, the treatment becomes complicated.
The patients with advanced stomach cancer consider participating in a clinical trial to help determine whether a new treatment is effective for treating them.
We advise some targeted drugs for treatment also. We may use targeted drugs in combination with chemotherapy drugs. Supportive care is provided by a team of doctors’ nurses and other trained professionals to help improve the quality of life for people with cancer.
Along with these medical professionals, the families’ supportive care with all the appropriate treatment may help people with cancer feel better and live longer.
